:quality(80))
Cyber Security Jobs Skills Radar 2026: Emerging Frameworks, Tools & Certifications to Learn Now
Cyber threats are evolving—and so must the people defending against them. As ransomware, AI-enhanced phishing, and supply chain attacks grow more advanced, UK employers are urgently hiring cyber security professionals with the right mix of strategic and hands-on skills.
Welcome to the Cyber Security Jobs Skills Radar 2026, your go-to guide for the most in-demand tools, frameworks, certifications, and technologies shaping the UK's cyber workforce. Whether you're a SOC analyst, penetration tester, or cloud security architect, this annual radar is designed to help you stay ahead of the market.
Why Cyber Security Skills Are Shifting in 2026
UK cyber teams are adapting to:
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and AI-assisted phishing
Cloud-native and container security
Board-level security governance and incident reporting
DevSecOps integration and shift-left principles
Regulatory pressure: GDPR, NIS2, DORA, ISO 27001
Employers want professionals who can detect, prevent, automate—and explain.
Top Technical Cyber Security Skills in 2026
1. Cloud Security (AWS, Azure, GCP)
What it is: Securing identities, workloads and cloud assets.
Why it matters: Cloud misconfigurations are still a top breach vector.
Used by: UK banks, NHS Digital, fintechs.
Roles: Cloud Security Engineer, DevSecOps Specialist.
Skills to pair: IAM, VPCs, GuardDuty, Azure Defender, GCP SCC.
2. Penetration Testing & Red Teaming
What it is: Offensive testing of applications, networks and endpoints.
Why it matters: Validates security posture, uncovers exploitable flaws.
Used by: Defence contractors, CREST-accredited firms.
Roles: Ethical Hacker, Application Security Engineer.
Skills to pair: Burp Suite, Metasploit, Cobalt Strike, Nmap.
3. SIEM & Threat Detection
What it is: Log ingestion, alerting, detection and forensic analysis.
Why it matters: SOC teams rely on real-time alerting.
Tools: Splunk, Microsoft Sentinel, QRadar, Elastic SIEM.
Roles: SOC Analyst, Detection Engineer.
4. Identity & Access Management (IAM)
What it is: Governing user permissions, SSO, and federation.
Why it matters: Compromised credentials remain the top attack vector.
Used by: Government and enterprise IT.
Skills to pair: MFA, conditional access, Okta, Azure AD.
5. Vulnerability Management
What it is: CVE scanning, prioritisation, patching and exposure tracking.
Why it matters: Builds proactive defence and hygiene.
Tools: Tenable Nessus, Qualys, OpenVAS, VulnDB.
Roles: Vulnerability Analyst, GRC Consultant.
Essential Security Frameworks & Platforms
1. MITRE ATT&CK
What it is: Knowledge base of adversarial tactics and techniques.
Why it matters: Used in threat modelling and detection engineering.
Roles: Threat Hunter, Blue Team Analyst.
2. SOAR Platforms
What it is: Security orchestration, automation and response.
Why it matters: Enables rapid triage and actioning of SIEM alerts.
Tools: Cortex XSOAR, Splunk SOAR, IBM Resilient.
3. EDR/XDR Tools
What it is: Endpoint (and extended) detection and response.
Why it matters: Core to incident response.
Tools: CrowdStrike Falcon, Microsoft Defender XDR, SentinelOne.
4. Zero Trust Architecture
What it is: Network model of continuous authentication and least privilege.
Why it matters: A modern requirement for hybrid work.
Vendors: Zscaler, Cloudflare, Palo Alto, Microsoft.
5. Open Source Tooling
Tools: Wireshark, OSQuery, Security Onion, Suricata.
Used by: Budget-conscious orgs, SOCs and forensic teams.
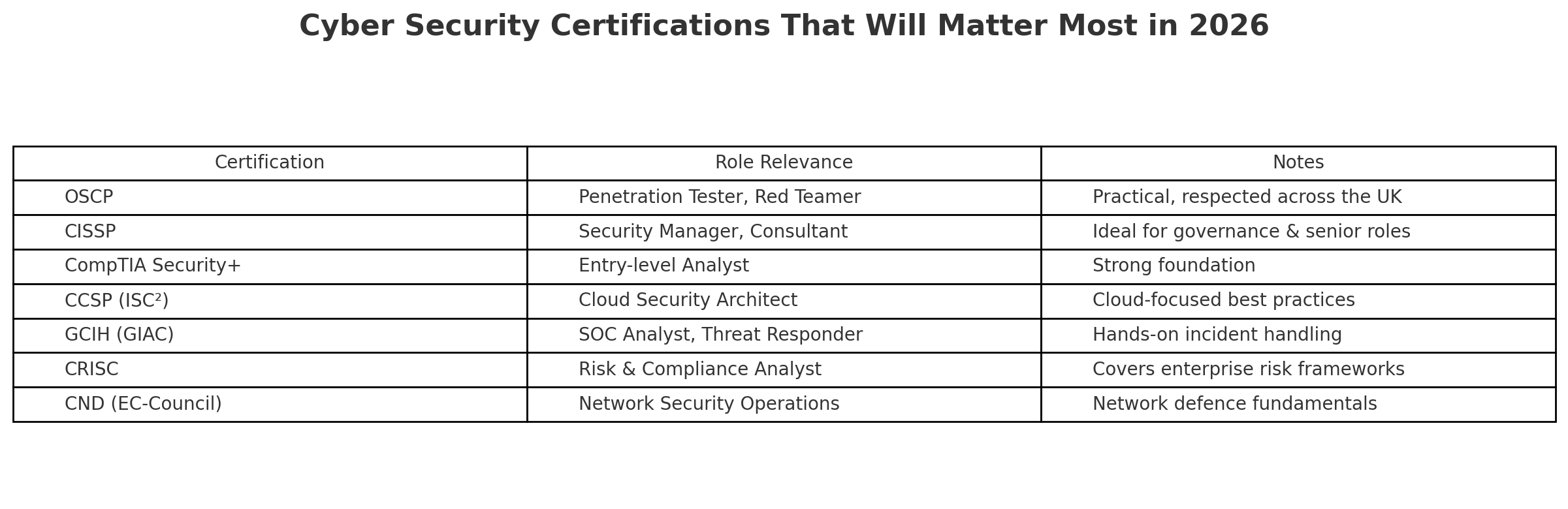
Cyber Security Certifications That Will Matter Most in 2026
Soft Skills & Strategic Competencies in Demand
Cyber incident response planning
Risk communication with executives
Vendor & third-party risk management
Regulatory compliance (GDPR, ISO 27001, NIS2)
Cyber security awareness training creation
AI, Automation & DevSecOps in Cyber Security
🔸 AI Threat Detection
What it is: Using ML to detect anomalies, behaviour drift, and threat actor patterns.
Tools: Vectra AI, Darktrace, Microsoft Security Copilot.
Roles: AI Threat Analyst, Behavioural Detection Specialist.
🔸 DevSecOps Integration
What it is: Embedding security into CI/CD and IaC.
Why it matters: Cloud-native apps must be secured at the pipeline level.
Tools: Snyk, SonarQube, Checkov, HashiCorp Sentinel, AWS Inspector.
Roles: DevSecOps Engineer, Cloud Security Developer.
🔸 OT & IoT Security
Why it matters: Critical infrastructure and smart homes/devices are now vulnerable endpoints.
Tools: Nozomi, Claroty, Dragos.
Roles: IoT Security Specialist, OT Defender, Embedded Security Analyst.
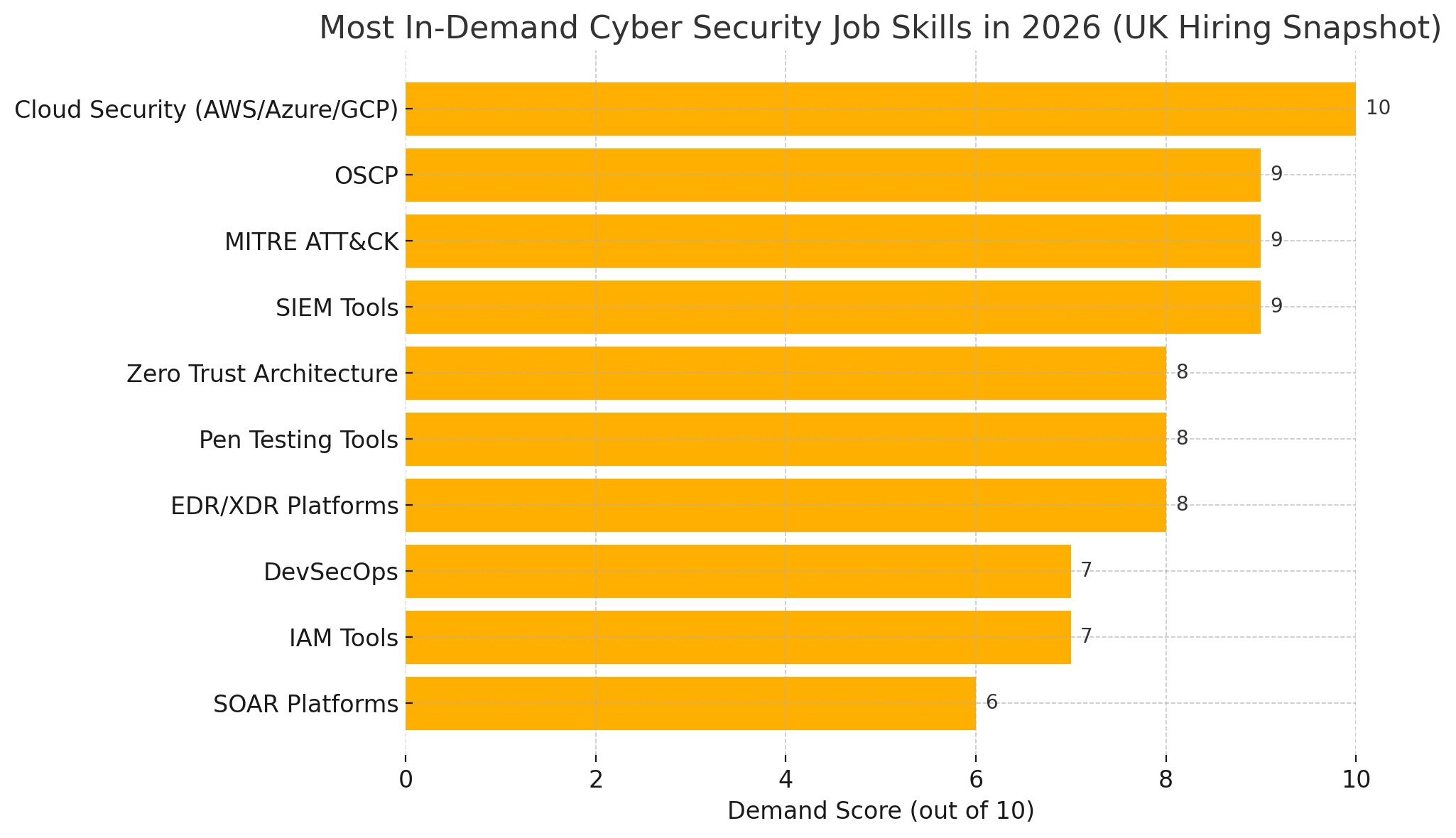
Most In-Demand Cyber Security Job Skills in 2026 (UK Hiring Snapshot Forecast)
Let’s visualise the top 10 cyber security tools, certifications & frameworks shaping hiring in the UK:
 How to Future-Proof Your Cyber Security Career in 2026
How to Future-Proof Your Cyber Security Career in 2026Pick a Specialism Early
Decide between red team, blue team, cloud security, GRC, or DevSecOps—and go deep.Certify and Practise
Certifications like OSCP or CCSP are valuable, but they must be backed by practical demos, labs, or GitHub projects.Keep Up with Tools & Threats
Follow MITRE ATT&CK updates, use TryHackMe or Hack The Box, and subscribe to threat intel briefings.Engage with UK Cyber Communities
Join BCS Cyber Security SIG, attend BSides, CYBERUK, and stay connected with CREST and Cyber Essentials forums.
Where to Find Cyber Security Jobs in the UK
🔐 Head to www.cybersecurityjobs.tech to find red teaming, SOC, cloud security, compliance, and cyber engineering roles across the UK. We highlight jobs from government, defence, finance, health tech, and scaleups.
Conclusion: Your Cyber Security Toolkit for 2026
Cyber security is a critical pillar of digital resilience in 2026. UK employers are hiring for tools that protect cloud, data, and infrastructure—so it's time to level up your toolkit with practical experience, certifications, and real-world application.
Use this Cyber Security Jobs Skills Radar 2026 as your north star—and return next year for an updated forecast of what’s hot in cyber hiring.
Subscribe to our newsletter for weekly job alerts, career advice, tool comparisons & free upskilling resources.


